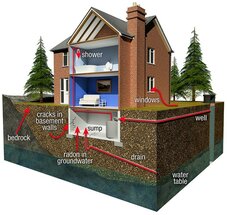
Radon Gas
More than 21,000 people die each year from radon exposure all over the United States. According to the Ohio Association of Radon Professionals, in Ohio, 1 in 2 households have enough radon to pose a significant risk to the occupants. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths than radon gas. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, your risk of lung cancer is especially high.
Because radon is invisible and odorless, the only way to know your home’s safety level is through proper radon tests. Accurate radon testing results can help you determine whether your home requires mitigation and how urgently action should be taken. Understanding your radon testing results is critical for protecting your family’s health, especially in high-risk areas.
If you have concerns about radon or need professional radon tests performed, now is the time to take action.
Visit our contact page today to get started!